Don't miss our updates


Guadalupe tenía 24 años cuando comenzó a buscar un tratamiento para tener hijos, pero su cuerpo se resistía al tratamiento. Ella te cuenta aquí.

Each year, on June 4, we celebrate World Fertility Day to remind everyone how valuable reproductive health is and to acknowledge the challenges faced by those who dream of starting a family. This date aims to inform about the causes of infertility and promote access to treatments and support that make a difference. At Ingenes, we join this global cause with advanced, personalized solutions to help you achieve your dream of becoming a mom or dad. Why is World Fertility Day important? Reproductive health is key to everyone’s well-being. According to the WHO, between 10% and 15% of couples face difficulties conceiving. Infertility often triggers intense emotions—frustration, sadness, and stress—that can affect daily life and relationships. Common causes and available treatments Infertility can arise from various factors in women and men, and sometimes it’s a shared challenge. Women: ovulation and reproductive anatomy Ovulation issues like PCOS, blocked fallopian tubes, or endometriosis are common. Diagnosis involves blood tests for hormones such as FSH and LH. Men: Sperm Quality and Quantity Problems in sperm production, blockages, or genetic causes can affect male fertility. A complete semen analysis provides essential information. Assisted reproduction techniques at Ingenes We offer intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in vitro fertilization (IVF) with ovarian stimulation of 75–150 IU/day of FSH. For specific cases, we provide ICSI and PGT, increasing success rates. Innovation that transforms lives With the IVF ABC program, our incubators maintain 37 °C and 5% CO₂ for optimal embryo development. We offer cryopreservation and advanced techniques that bring hope to many families. Discover more at Celebrating Hope and Science on World Fertility Day and at World Sexual Health Day: A Holistic View of Wellness and Fertility. Frequently Asked Questions When Should You See a Fertility Specialist? If you’ve been trying to conceive for 12 months (or 6 months if you’re over 35) without success, it’s time to consult a reproductive specialist. They will review your history, request hormonal tests, and order imaging studies such as ultrasounds. Do not self-medicate: a specialist will determine precise doses and monitor your treatment to maximize your chances and safeguard your health. What Are the Success Rates for IVF and ICSI? In women under 35, implantation of a quality embryo can exceed 40% per IVF cycle. ICSI fertilizes between 70% and 80% of oocytes when semen analysis shows abnormalities. Using PGT to select viable embryos can boost these figures, but every case is unique and requires a personalized plan. What Side Effects May Occur? Ovarian stimulation can cause ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), bloating, and breast discomfort. With controlled FSH doses (75–150 IU/day) and frequent monitoring, the risk decreases. Follicular puncture is usually performed under sedation and is well tolerated. Report any unusual symptoms to your medical team. Is It Worth Freezing Eggs or Embryos? Vitrification offers reproductive freedom to those wishing to postpone motherhood. Post-thaw survival exceeds 90%. Your specialist will assess your ovarian reserve with AMH hormone levels and recommend the best strategy. The procedure lasts under 60 minutes and, with local anesthesia, is comfortable and safe. Sources World Health Organization. (2020). Infertility definitions and terminology. Retrieved from https://www.who.int American Society for Reproductive Medicine. (2019). Optimizing Natural Fertility. Fertility and Sterility, 111(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.11.013 National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. (2021). Assisted Reproductive Technology. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. (2022). Criteria for PGT-A. Fertility and Sterility, 117(2), 234–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2021.10.027 We know this journey can be challenging. You are not alone: with proper support and a fertility specialist, you will increase your chances of achieving that long-awaited pregnancy. Consult a professional to receive the guidance and support you need.
The seminal tract is the path that sperm take from the testes to the outside. If an infection occurs at any point along this route, the inflamed areas can damage semen quality and make it harder for the egg to be fertilized. The good news is that most of these infections respond very well to antibiotics. If semen quality remains low after treatment, in vitro fertilization with ICSI is usually the best option to achieve pregnancy. What are seminal infections and how do they affect your fertility? Seminal infections arise when bacteria, fungi, or viruses reach the prostate, seminal vesicles, epididymis, or vas deferens. This can cause: Obstruction of seminal flow, causing azoospermia (absence of sperm) or oligozoospermia (fewer than 15 million/mL). Reduced sperm motility (asthenozoospermia). Abnormal sperm morphology (teratozoospermia). Increased sperm DNA fragmentation, making implantation more difficult. Production of antibodies against sperm. Possible transmission of the infection to your partner. What are the symptoms? They are often silent and only detected through a fertility study, but sometimes they present with: Changes in semen color or consistency. Irritation, itching, or burning when urinating. Urethral discharge. Discomfort in the perineal or testicular area. Avoid self-medication. If you notice any of these symptoms, stop sexual activity and consult an assisted reproduction specialist. Why do they occur? The most common causes are sexually transmitted bacteria (Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae) or intestinal flora (such as Escherichia coli or Enterococcus faecalis). The risk is higher with unprotected sex or multiple partners. Factors that increase the likelihood: Poor genital hygiene. Invasive urological procedures. Weakened immune system. How is it diagnosed? The specialist usually: Takes your medical history and performs a physical exam. Performs a urine culture and semen culture with antibiotic sensitivity. Orders molecular tests (PCR). Analyzes the semen with a semen analysis and DNA fragmentation test. With this information, a personalized treatment plan is designed and follow-up studies are performed to confirm that the infection has cleared. Treatment and options for achieving pregnancy Initial treatment is usually oral antibiotics for 7–14 days. It is essential that both you and your partner complete the course and maintain sexual abstinence during the medication period. Once the infection is eradicated, sperm quality is reassessed. If problems persist (concentration < 15 M/mL, motility < 40%, or high fragmentation), IVF+ICSI or additional tests in our fertility laboratory are considered. Frequently Asked Questions 1. Do they always cause infertility? No. Many are detected and treated in time, restoring semen quality. However, if inflammation becomes chronic, it can cause scarring and blockages, leading to persistent oligozoospermia or asthenozoospermia. Consult as soon as you notice any symptoms. 2. Can I infect my partner during treatment? Yes, which is why both partners should be treated simultaneously. Abstinence and condom use after therapy help prevent reinfection. 3. How does DNA fragmentation affect things? If it exceeds 30%, it can hinder natural fertilization and increase the risk of miscarriage. In those cases, ICSI along with prior antioxidant supplements is recommended. 4. Can they be prevented? With safe sexual practices (condom use), good genital hygiene, and regular check-ups if you have risk factors. A healthy lifestyle (balanced diet, exercise, no smoking) also strengthens your immune system. Sources National Library of Medicine. (2023). Male reproductive system infections. MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov World Health Organization. (2021). WHO laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human semen (6th ed.). Geneva: WHO Press. Dohle, G. R., Diemer, T., Kopa, Z. (2019). EAU Guidelines on Male Infertility. European Urology, 76(4), 616–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2019.08.029 Esteves, S. C., Agarwal, A. (2020). Role of oxidative stress in male infertility. Clinics, 75, e1909. https://doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2020/e1909 Remember that each case is unique. If you are looking to start a family, do not hesitate to consult an assisted reproduction specialist: we are here to support you every step of the way.
A recent study published in the American Journal of Translational Research titled “Improving Endometrial Thickness and In Vitro Fertilization Outcomes in Patients with Refractory Endometrium Using Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cells” presents a novel technique to enhance in vitro fertilization in complex infertility cases. Researchers such as Dinorah Hernández-Melchor, Ginna Ortiz, and Iván Madrazo from the Ingenes specialist team, along with other collaborators, succeeded in using stromal vascular fraction stem cells to restore endometrial thickness in refractory patients. This opens new possibilities for treating infertility in these cases. The article examines how endogenous stem cells (ENDOGEN) can improve oocyte quality and increase the chances of obtaining a viable embryo in patients who have had multiple failed IVF attempts. This breakthrough could mark a turning point in infertility management, especially when egg quality is a challenge. Preliminary results show that patients produce more healthy embryos, suggesting that ENDOGEN could become a standard tool in assisted reproduction, reducing the need for more invasive procedures such as egg donation. What is ENDOGEN and what is it used for in Fertility and IVF? ENDOGEN consists of autologous mesenchymal stem cells extracted from the stromal vascular fraction. They are applied to the uterus to regenerate the endometrium and increase its thickness. Their main function is to optimize the environment where the embryo will implant, raising implantation rates and IVF success chances. How does ENDOGEN improve oocyte quality in patients with previous failures? This therapy increases endometrial vascularization and uterine receptivity, benefiting oocyte maturation and cell communication. By improving the microenvironment, follicular cells receive the necessary nutrients and growth factors to generate high-quality embryos. Benefits and risks associated with ENDOGEN treatment Benefits: An increase of 2 to 3 mm in endometrial thickness. Higher embryo implantation rate. Reduced need for egg donation. Risks: Mild inflammation at the injection site. Minimal risk of rejection or adverse reaction. Steps to follow after the ENDOGEN procedure After application, an ultrasound follow-up every 7–10 days is recommended to measure endometrial thickness and assess response. Once the endometrium reaches at least 7 mm, embryo transfer is scheduled. Do not self-medicate: always consult your doctor. Integration with other assisted reproduction therapies ENDOGEN can be combined with conventional ovarian stimulation protocols, tailored to each patient. Consult an Assisted Reproduction specialist to plan the best path to your pregnancy. Recommended links for further reading Learn more about The Scientific Impact of Ovagen and Endogen and explore Advances in Reproduction: An Innovative Path for Future Parents. Patient testimonials after receiving ENDOGEN Many women report feeling more comfortable during embryo transfer and experiencing a more receptive endometrium. Others mention quicker recovery and fewer discomforts. Comparison of ENDOGEN with other stem cell therapies Unlike allogeneic therapies, ENDOGEN uses your own cells, virtually eliminating the risk of rejection and immunological complications, and avoiding the need for external donors. Sources Consulted Hernández-Melchor, D., Ortiz, G., & Madrazo, I. (2024). Improving endometrial thickness and in vitro fertilization outcomes in patients with refractory endometrium using autologous mesenchymal stem cells. American Journal of Translational Research, 16(8), 560–575. https://doi.org/10.1000/ajtr0156075 MedlinePlus. (2023). Stem cell transplantation. https://medlineplus.gov/stemcelltransplantation.html National Library of Medicine. (2022). Endometrial thickness and IVF outcomes. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa202123 World Health Organization. (2021). WHO laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human semen (6th ed.). https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240030787 Remember that each case is unique. If you are considering this treatment or any other assisted reproduction technique, rely on the support of a fertilization specialist. You are not alone on this journey!

Hydrosalpinx is a condition in which one or both fallopian tubes become filled with fluid, usually due to a previous infection or inflammation. This fluid, which can be toxic to embryos, poses a significant challenge for women seeking In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) treatments. When hydrosalpinx is present, the built-up fluid can leak into the uterus, decreasing IVF success rates and may even prevent embryo implantation. What is hydrosalpinx and how does it affect fertility? Hydrosalpinx develops when a fallopian tube becomes blocked and filled with serous fluid. This condition is often the result of previous infections, such as pelvic inflammatory disease, or surgery in the pelvic area. Although not all women with hydrosalpinx experience symptoms, some may notice pelvic pain, abdominal swelling, or abnormal vaginal discharge. The main problem with hydrosalpinx in the context of IVF is that the toxic fluid that builds up in the tubes can leak into the uterine cavity. Not only can this fluid prevent the embryo from implanting properly, but it can also directly damage the embryo, drastically reducing the chances of a successful pregnancy. For these reasons, it is crucial to address hydrosalpinx before starting an IVF cycle. Strategies to improve IVF success rates in the presence of hydrosalpinx When a woman is diagnosed with hydrosalpinx and is planning to undergo IVF treatment, there are several strategies to improve the chances of treatment success. Although solutions may vary from case to case, one of the most common recommendations is to perform a hysteroscopy to create a blockage in the tubal orifices. This procedure helps prevent toxic fluid from the fallopian tubes from reaching the uterus, thereby protecting the developing embryo. During hysteroscopy, the doctor inserts a small instrument through the cervix to access the inside of the uterus and fallopian tubes. It is used to block the tubal orifices, preventing fluid from passing into the uterus. This procedure is minimally invasive and can be very effective in improving implantation and pregnancy rates in women with hydrosalpinx. In more severe cases, where the hydrosalpinx is larger than 3 cm or where there is severe damage to the fallopian tube, laparoscopic surgery may be necessary to remove the affected tube. Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgery that allows the doctor to access the pelvic area through small incisions and with the aid of a camera. Although removing a fallopian tube may seem like a drastic measure, in many cases it is the best option to increase IVF success rates and avoid future fertility problems. Considerations before treatment Women with hydrosalpinx must receive a thorough diagnosis and proper evaluation before starting any fertility treatment. At Ingenes Fertility Institute in Mexico, the personalized approach and advanced technology allow specialists to offer recommendations based on each patient’s specific needs. Ingenes advises patients on the best options available to optimize the results of their treatments. In addition, women must maintain an open dialogue with their medical team about any concerns or symptoms they may experience. This ensures that any complications, such as hydrosalpinx, are managed in a timely and effective manner, thereby protecting the chances of success in IVF. Hydrosalpinx can have a significant impact on IVF success rates due to the presence of toxic substances in the fluid accumulated in the fallopian tubes. However, with proper diagnosis and correct management, it is possible to mitigate its effects and improve the chances of a successful pregnancy. Hysteroscopy to create a tubal blockage and laparoscopic surgery to remove the damaged tubes are viable options that can be considered depending on the severity of the case. As a leader in fertility treatments, Ingenes Fertility Institute in Mexico offers guidance and advanced solutions to help women overcome these challenges and get one step closer to their goal of starting a family. Patients must educate themselves and consult with specialists to make informed and personalized decisions.

Within these conditions, vaginal infections such as Bacterial Vaginosis (BV) are one of the first causes of consultation for women of reproductive age. (Approximately 95% of patients who go to the gynecologist do so because of some type of infectious vaginal discharge). Vaginal infections affect women’s fertility since they belong to a large group of pathologies that generate varied clinical symptoms, ranging from uncomplicated processes to severe symptoms such as septic symptoms, which can compromise the lives of patients. When there is the presence of a vaginal infection, symptoms such as itching, irritation, and bad odor occur. However, it is very difficult to distinguish these infections from each other based only on the symptoms, and it is absolutely necessary to perform an examination and a microbiological study to establish the diagnosis. Speaking specifically about Bacterial Vaginosis (BV), it is first necessary to understand the function of the Normal Vaginal Flora, composed of microorganisms found in the vagina that, shortly after birth, change their constitution permanently throughout life. life in all women. Although efforts have been made to determine the characteristics of the microorganisms that compose it, there is still no absolute clarity of all the commensal agents of the Normal Vaginal Flora. However, the presence of BV is associated with a greater risk of infection in the upper genital tract and sexually transmitted infections such as HIV, affecting a third of sexually active women in the world. In addition to this, among the most common pelvic conditions we have Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID), which is a polymicrobial infectious pathology, caused by both sexually transmitted microorganisms and other bacteria that ascend from the vaginal tract to the pelvic structures. PID encompasses inflammatory and infectious processes of the upper genital tract and can be part of the following conditions: In pregnancy, BV is associated with spontaneous abortion, premature rupture of membranes, preterm delivery, chorioamnionitis, and postpartum endometritis. Fortunately, there are alternatives for those women who have had vaginal infections that have already impacted their fertility and who want to have a baby. The most effective technique is In Vitro Fertilization since it is the treatment that has the highest percentage of success and the best results. Ingenes Institute has several years of experience treating the largest number of and most complex fertility cases, so our team of specialists has all the experience to deal with infertility cases.

Guadalupe utilizó el método ROPA para quedar embarazada y ser madre de Matías junto a su esposa. Un bebé de ambas, conoce su historia aquí.

Después de 5 años de intentarlo, Claudia logró tener a su bebé mediante una Fertilización In Vitro. Conoce su historia.
At Ingenes we have a sperm bank designed to support couples with male infertility and single women who wish to become mothers. Here we select, evaluate, and store secure samples so you can build your family with the peace of mind of high quality standards. We offer donors of various races and characteristics, so you can find the profile that best suits you. All samples are processed according to the guidelines of the ASRM, the WHO and Mexican regulations. Additionally, you can freeze your own sperm to use later in your treatments. What is a sperm bank and how does it support assisted reproduction? Sperm donation is key for: Couples with azoospermia or low sperm quality Men with severe motility or morphology issues Preventing transmission of genetic diseases Single women who want to become mothers At Ingenes your samples undergo medical and psychological tests, karyotype analysis, and viability tests after freezing. They remain in quarantine for 6 months to rule out infections like HIV before release. Donor selection and evaluation Our donors are mainly young university students. We accept only a small percentage after these tests: Complete medical exam (blood group, karyotype, infection screening) Psychological evaluation and lifestyle questionnaire Motility, morphology and concentration analysis according to WHO standards Survival tests before and after freezing Benefits of semen storage Cryopreservation is ideal if you are going to: Undergo chemotherapy or radiotherapy Take medications or have surgeries affecting your testicles Suffer from chronic diseases like diabetes or multiple sclerosis Plan a vasectomy Undergo sperm retrieval procedures Travel during your assisted reproduction cycles We analyze each sample before freezing, perform a viability test and tell you how many vials you will need. Thanks to ICSI, good results can be achieved even with few viable sperm. Sample safety and integrity We store semen in liquid nitrogen at –196 °C indefinitely. Our labeling and storage protocols prevent mix-ups. We advise you on donor type, number of samples, and the complete process, including emotional support sessions (discover our emotional support). More information about assisted reproduction Visit our Frequently Asked Questions to clear doubts about procedures, timing, costs, and emotional support. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. Can I choose physical characteristics of the donor? Yes, you can specify traits like height, eye color, and ethnic background. However, it is crucial to prioritize genetic and blood group compatibility to reduce hereditary risks. The process is anonymous and confidential. 2. How long can sperm be stored frozen? It remains preserved indefinitely if kept in liquid nitrogen at –196 °C. Studies confirm successful pregnancies with samples stored for over 20 years. 3. What are the risks of donation? It is a non-invasive procedure; the main risk is minimal and related to sample collection. We follow a strict biosafety protocol and offer emotional support for your peace of mind. 4. What if I don’t achieve pregnancy with donated sperm? Success rates vary depending on age and egg quality. If after 2–3 cycles there’s no pregnancy, we review your case and recommend adjustments in treatment, donor profile, or alternative treatments like egg donation. Sources consulted American Society for Reproductive Medicine. (2021). Guidelines for sperm donor selection. ASRM. World Health Organization. (2021). WHO laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human semen (6th ed.). WHO. National Library of Medicine. (2020). Semen Cryopreservation. MedlinePlus. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. (2022). Advances in sperm banking. Fertility and Sterility, 117(3), 515–523. We know how important this step is for you. We support you with professionalism and warmth. Always consult a fertility specialist for the best personalized guidance.

¿Se puede quedar embarazada con quistes en los ovarios? Conoce a Rosy, una mujer de más de 35 invadida de quistes, y cómo logró a su bebé.

Silvia fue mamá después de los 40 años con una Fecundación In Vitro, pero la gran sorpresa fue que año y medio después se embarazó de nuevo sin ayuda.
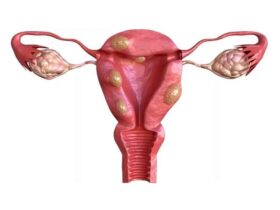
Uterine myomatosis is the formation of myomas or fibroids inside the uterus. These are benign tumors classified according to their location. Depending on where they are found, fibroids are classified as: Intramural: within the muscular wall of the uterus. They can affect fertility if they exceed 4 cm. Submucosal: on the surface of the uterine lining. They hinder embryo implantation. Subserosal: in the outer layer of the uterus. They usually do not interfere with fertility. What is uterine myomatosis and why does it matter for fertility? Uterine myomatosis involves the growth of fibroids, benign smooth muscle tumors, inside the uterus. It affects about 20% of women of reproductive age, especially after age 30. Fibroids can range from microscopic nodules to masses over 4 kg, altering the shape of the uterus and reducing pregnancy chances. How common is uterine myomatosis in those trying to conceive? Uterine fibroids are the most common pelvic tumors in women of reproductive age, present in nearly 70–80% before menopause. Although many are asymptomatic, those that deform the uterine cavity—particularly large intramural and submucosal fibroids—are involved in up to 80% of uterine factor infertility cases. How do fibroids affect embryo implantation? Large submucosal and intramural fibroids can: Alter sperm transport and uterine peristalsis Reduce endometrial receptivity by compressing the lining Increase the risk of implantation failure and early miscarriage Can fibroids complicate pregnancy? Yes. During pregnancy, fibroids can cause: Higher risk of miscarriage and preterm birth Fetal growth restriction due to lack of space Cervical canal obstruction or labor dystocia Postpartum hemorrhage from poor uterine contraction What symptoms may indicate fibroids? About 25% are asymptomatic. When symptoms occur, they include: Sensation of pelvic pressure or heaviness Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding Pelvic cramps and irregular bleeding Frequent urination or difficulty urinating Secondary infertility or recurrent miscarriages Severity depends on fibroid size, number, and location. How is diagnosis confirmed? Transvaginal ultrasound is the gold standard, with nearly 100% sensitivity (95% transabdominal). In complex cases, MRI is used. Always consult a reproductive medicine specialist to interpret results and design a treatment plan. Fertility-preserving treatment options Choice depends on age, fibroid characteristics, and reproductive goals: Expectant management for small, asymptomatic fibroids Myomectomy (surgical removal), followed by assisted reproduction techniques Controlled ovarian stimulation combined with in vitro fertilization (IVF) if cavity distortion persists IVF bypasses uterine transport obstacles and allows for selecting the embryo with the highest implantation potential. For more information, see our guide on Endometriosis: what it is and how it impacts fertility. FAQ 1. Can small fibroids disappear on their own? Yes. Many remain stable or shrink after menopause due to estrogen decline. In reproductive age, asymptomatic fibroids under 2 cm are usually monitored with periodic ultrasounds. If you plan to conceive, even a small submucosal fibroid can affect implantation, so consult your doctor to assess intervention before trying to conceive. 2. Are there non-surgical treatments? GnRH agonists and selective progesterone receptor modulators can temporarily shrink fibroids and reduce bleeding in 3–6 month cycles. They improve conditions before surgery or comfort but are not definitive solutions. Never self-medicate without medical supervision. 3. When can I attempt IVF after a myomectomy? Ideally between 6 and 12 months after surgery, before recurrence risk increases. This timing allows the uterine lining to heal and optimizes pregnancy chances. Make sure your specialist confirms proper healing with ultrasound or hysteroscopy before starting treatment. 4. Does the risk of miscarriage increase? Yes. Fibroids that deform the cavity or alter blood flow are associated with early pregnancy loss. Risk increases with fibroid size and location, especially submucosal and large intramural fibroids. Proper management, surgical or with assisted reproduction, significantly reduces miscarriage rates. Always consult a specialist before making decisions. References Faerstein, E., Szklo, M., & Schwingl, P. J. (2001). Risk factors for uterine leiomyoma: a practice-based case–control study. American Journal of Epidemiology, 153(5), 463–469. doi:10.1093/aje/153.5.463 Lau, W., & Shlisselberg, S. (2016). Management of uterine fibroids. American Family Physician, 94(2), 106–113. https://www.aafp.org/afp/2016/0715/p106.html MedlinePlus. (2021). Uterine fibroids. https://medlineplus.gov/uterinefibroids.html Stewart, E. A. (2015). Uterine fibroids. Lancet, 376(9745), 145–157. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60246-1 Remember: every body is unique. Stay informed, keep hope, and consult an assisted reproduction specialist for personalized care.

Having a baby means thinking about its health. Learn about the test that anticipates and dismisses congenital anomalies in babies.

Clara tiene útero retroverso, como 1 de cada 5 mujeres. Conoce su historia y cómo se transformó en mamá cuando tenía más de 39 años.

A mother carrying a baby in her womb alters its genes, even when the egg comes from another woman. This means her child will be born with traits similar to hers, according to a study by the Valencia Infertility Institute Foundation (IVI). How does the maternal uterus influence the genes of a donated embryo? The uterus is much more than a container: during gestation there is constant dialogue between embryo and endometrium. Endometrial fluid exosomes release maternal RNA that reaches the embryonic nucleus and regulates gene expression, adjusting physical and health traits. Studies such as “The Marvelous Science of Egg Donation: Beyond Genes” explain this in detail. Electron microscope of an exosome about to adhere to the endometrium (IVI). For nine months, the embryo receives blood, nutrients, and oxygen through the umbilical cord. These biochemical signals vary according to the gestational carrier’s genetics, habits, and lifestyle, reinforcing that egg donation is only the starting point. It is the uterus that shapes and “signs” the DNA that will guide the baby’s development. What epigenetic changes can gestation cause in egg donation? During gestation, epigenetic interaction can influence: Eye color and shape Hair texture and tone Facial expressions, such as the smile Predisposition to certain metabolic or autoimmune diseases These modifications do not replace the donated genetics but regulate the activation or silencing of specific genes. To learn more, see “The Revolutionary World of Fertility and Egg Donation”. How does genetic exchange occur between embryo and endometrium? Exosome releasing maternal RNA into the cytoplasm of a blastocyst (IVI). Exosomes, 50–150 nm vesicles, transport maternal RNA to the blastocyst’s cytoplasm and adjust gene transcription. The result is a unique epigenetic profile that combines the donor’s inheritance and the carrier’s influence. Why is egg donation a great opportunity? Rocío, 52, had her two babies via egg donation at Ingenes. The egg donation experience lets you carry and give birth to a child with a unique maternal genetic imprint. Avoid self-medication and always consult a Assisted Reproduction specialist before starting any fertility treatment. Frequently Asked Questions about egg donation and uterine genetics 1. Does the gestational mother contribute DNA if the eggs are from another person? Yes. Although the main genetic load comes from the donor, during gestation the uterus releases exosomes with RNA that modulate the embryo’s gene expression, influencing physical traits and future health. 2. What risks or benefits does this genetic interaction have? Benefits include better embryo adaptation to the uterine environment and higher implantation rates. As for risks, long-term impact is still under study: so far there is no evidence of adverse effects, but specialized prenatal follow-up is recommended. 3. Can it influence the baby’s temperament? Personality arises from genetics and environment. Egg donation and uterine influence affect physical traits and biochemical predispositions, but parenting style and the postnatal environment are key to the child’s character. 4. How to choose the best clinic for egg donation? Choose centers with international accreditations, multidisciplinary teams, and evidence-based protocols. Review their success rates, lab technology, and psychological support offered before and after birth. Sources Vilella F. et al. (2015). Hsa-miR-30d, secreted by the human endometrium, is taken up by the pre-implantation embryo and might modify its transcriptome. Development, 142(18), 3210–3221. MedlinePlus. (2023). Assisted Reproductive Technology. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Gardiner K. et al. (2020). Epigenetic modifications during pregnancy: maternal-fetal interactions. Journal of Reproductive Immunology, 138, 103-110. Mor & Cardenas. (2018). The immune system in pregnancy: a unique complexity. American Journal of Reproductive Immunology, 79(3), e12847. We are with you on this journey. If you have questions or are considering egg donation, consult an Assisted Reproduction specialist for the best guidance and support.

What is the reality of fertility today? Although we don’t talk about it every day, facing difficulties conceiving is more common than you think: 1 in 6 couples experiences it. The good news is that science and medicine have advanced greatly and offer real solutions to fertility challenges. Why do fertility problems arise? Reproductive challenges can stem from different factors: ovulatory, tubal-peritoneal, uterine, or male (for example, low sperm quality or quantity). Lifestyle habits such as smoking, stress, a very high BMI (>30 kg/m²) or very low (

El Método ROPA en México es una opción de Reproducción Asistida que permite a las parejas de mujeres convertirse en madres biológicas.
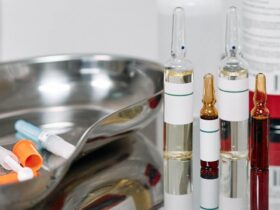
Most fertility medications are administered subcutaneously. This means that they are applied with a very small needle that only penetrates the skin, so they are painless. Medications to stimulate egg production must be prescribed by a fertility specialist and their effects must be carefully monitored through transvaginal ultrasounds and blood tests every two to three days. If you are about to undergo an assisted reproduction treatment such as In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), you must apply medications to stimulate your egg production and thus maximize your chances of pregnancy so that you have a baby. It is normal to feel nervous before the first application. This is usually the first time that most women inject themselves and the fear of not doing it right adds to the emotions they face due to their struggle with infertility. How to apply the medications? The process of applying fertility medications consists of following simple steps: Medication Tips Normal effects of the medication. During this process, you will have to undergo transvaginal ultrasounds and blood tests every two or three days. These allow you to monitor the development of the follicles (sacs that contain the eggs) and monitor your reaction to the medications. The medications cause some effects that are considered normal, including mood changes, breast engorgement, and headaches in very rare cases. For their part, if these medications are applied without the supervision of a specialist who monitors the patient’s progress, they can cause ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, which affects less than 1 percent of patients. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome manifests itself with symptoms such as fever, nausea, fluid retention, and abdominal distention (which usually appear after egg retrieval or follicular aspiration). You should be treated by a specialist to avoid complications. It is very important that you contact the fertility specialist if you present any of these symptoms, if you have doubts regarding the application of medications, or if you administer a higher dose than indicated. Other symptoms that may occur are irritation in the application area or infection, in which case it is also important that you contact your doctor. Most common medications Your diagnosis and treatment plan will determine the combination of injectable medications you will require in each IVF cycle. Some of the most used are: Remember that before administering any medication it is very important that you have a diagnosis from a specialist, since it is the one indicated to monitor the evolution of the medications and will be your guide during the process until you manage to have a baby at home.

In in vitro fertilization (IVF), science and hope unite for those dreaming of welcoming a baby. We explain the process from start to finish. How is in vitro fertilization performed step by step? 1. Ovarian stimulation: you receive hormones (150–300 IU of FSH/LH) so your ovaries develop multiple follicles. 2. Follicular puncture: under light sedation, mature eggs are retrieved with an ultrasound-guided needle. 3. Semen preparation: we collect a 2–5 mL sample and select the most motile sperm. 4. In vitro fertilization: oocytes and sperm are placed together in a ~100 µL culture medium. After 16–18 h the zygote forms, and at 48 h it becomes a 4–8 cell embryo ready for transfer. When is IVF recommended? Damage or blockage of the fallopian tubes. Moderate to severe endometriosis. Severe male factor (low count or motility). Women ≥35 years with reduced ovarian reserve. Failures in other fertility treatments. Before starting, consult an assisted reproduction specialist; they will tell you if this treatment is the best path for you. Preparation for your IVF cycle Your doctor will request hormonal tests (FSH, LH, AMH), a transvaginal ultrasound, and a semen analysis. Adopt a healthy lifestyle: balanced diet, moderate exercise, and stress management. Avoid tobacco and alcohol at least 3 months beforehand. You can also seek nutritional counseling and psychological support to feel accompanied at every stage. Follicular puncture and fertilization The puncture takes 20–30 minutes with local anesthesia or sedation. An average of 8–15 eggs are retrieved. In the lab, we assess quality and fertilize them by conventional IVF or ICSI, depending on your case. Embryos grow in incubators at 37 °C, 5 % CO₂, and 95 % humidity until reaching the blastocyst stage (day 5). Embryo transfer and beyond Between day 3 and 5, we select 1–2 top-quality embryos and deposit them in your uterus under ultrasound guidance. The procedure is brief; afterward you’ll rest for 24–48 h and receive progesterone (600 mg/day vaginally or 50 mg IM). Two weeks later, a serum beta-hCG test is performed. If positive, you continue hormonal support until weeks 10–12 of gestation. For a deeper dive into each phase, visit Understand in vitro fertilization step by step and Understand in vitro fertilization. Frequently asked questions 1. What influences success rates? Maternal age (<35 years up to 40% success vs. 20% at 40), egg and sperm quality, and lab experience. Lifestyle habits, body mass index, and infertility causes also matter. 2. Does it hurt or carry risks? The main discomfort is the follicular puncture, managed with sedation. Hormonal injections may cause mild discomfort. Risks: ovarian hyperstimulation (1–5%), mild bleeding or infection, and multiple pregnancy if multiple embryos are transferred. 3. Can I use donors? Yes, if your ovarian reserve or sperm quality is low. Donors undergo genetic, infectious, and psychological screening. The IVF protocol is the same; only the gametes change. 4. When will I know if I’m pregnant? You wait 10–14 days post-transfer for the beta-hCG test. If positive, a heartbeat is confirmed by ultrasound at 5–6 weeks and obstetric follow-up begins. Sources American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Practice Committee Guidelines. Fertility and Sterility (2021). MedlinePlus. In Vitro Fertilization. U.S. National Library of Medicine (2022). European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology. Vienna Consensus on GnRH analogue protocols in ART (2020). National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Fertility: Assessment and treatment (2017). Remember: each path to parenthood is unique. If you have questions or want more information, consult an assisted reproduction specialist. You are not alone on this journey!

El clomifeno es un medicamento que promueve la ovulación, y puede incrementar las probabilidades de un embarazo si es administrado de forma adecuada por médicos especialistas. Te explicamos cómo aquí.

Human somatic cells are diploid, they normally have 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 chromosomes), in which all the genes that make up the genome are distributed. Sex cells (eggs and sperm) are haploid and only contain half as many chromosomes. What is an aneuploidy? A cell that contains a normal chromosome load is known as euploid and when it has an abnormal number of chromosomes due to gains or losses in one or more chromosomes, it is called aneuploid. When the abnormal number results in a number of chromosomes less than 46 it is known as monosomy, while when there is a gain of chromosomes it is known as trisomy (more than 46). What are the causes? Most chromosome duplication and deletion errors originate during gametogenesis, mainly in oogenesis (during meiosis I), while another considerable percentage of errors arise during the first mitosis after fertilization. Around 50% of all embryos produced through assisted reproduction techniques are aneuploid, the rate of aneuploidy increases as maternal age increases. From the age of 37, a higher percentage of aneuploid embryos is produced. The trisomies most frequently found in IVF embryos are 16, 19 and 21, while monosomy 22 and partial loss of the Y chromosome are the most common monosomies. All monosomies (except X chromosome monosomy or Turner syndrome) are incompatible with life; However, all trisomies can give rise to a baby with serious health problems. The type of involvement, phenotypic characteristics and life expectancy of the affected individual will depend on the type of trisomy. Trisomy 21, for example, a condition that gives rise to Down syndrome and one of the most frequent trisomies (1 case in 700 occurs), is characterized by a phenotype prone to congenital heart disease, mental retardation of varying degrees, and a long life expectancy. average of 50 years. Why does it impact fertility? Around 35% of all implantation failures that occur in assisted reproduction treatments are due to the transfer of aneuploid embryos. Additionally, in a study carried out at our Institute, it was determined that a mostly aneuploid embryonic cohort negatively affects the implantation result. Alternative ways to having a baby without this condition posing a barrier Recommending and carrying out Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD Ingenes) for all embryos achieved through IVF to know their chromosomal profile will avoid the transfer of aneuploid embryos. This behavior will increase the chances of implantation and pregnancy. PGT should be performed on all embryos during In Vitro Fertilization, especially if the woman’s age is over 37, or if the couple has a family history of aneuploidies. Sources Hassold, T., and Hunt, P. (2001). To err (meiotically) is human: the genesis of human aneuploidy. Nature reviews Genetics 2, 280-291. Ramia, M., Musharrafieh, U., Khaddage, W., and Sabri, A. (2014). Revisiting Down syndrome from the ENT perspective: review of literature and recommendations. European archives of oto-rhino-laryngology : official journal of the European Federation of Oto-Rhino-Laryngological Societies 271, 863-869. Rubio, C., Bellver, J., Rodrigo, L., Castillon, G., Guillen, A., Vidal, C., Giles, J., Ferrando, M., Cabanillas, S., Remohi, J., et al. (2017). In vitro fertilization with preimplantation genetic diagnosis for aneuploidies in advanced maternal age: a randomized, controlled study. Fertility and sterility 107, 1122-1129.
Una reserva ovárica baja puede comprometer tus probabilidades de tener un bebé. Te decimos cómo conocer la tuya y tus opciones para ser mamá.

Las mujeres con ovario poliquístico pueden tener hijos. Claudia te cuenta cómo ella lo logró después de buscar a su bebé por más de 5 años.

Con el método ROPA de fertilización in vitro, las parejas de mujeres pueden tener un bebé de ambas: el óvulo de una en el vientre de la otra.

Una mala calidad de óvulos no impide que tengas un bebé. Iraí te comparte su camino y el tratamiento específico que la ayudó a lograrlo.

Starting the journey to parenthood is exciting, but it can also raise questions about how to prepare. At Ingenes we guide you with a clear, approachable guide covering all aspects—physical, emotional, and lifestyle—to plan your pregnancy with confidence. First medical steps before conceiving Before trying to conceive, the most important step is to consult a fertility specialist. Together you’ll review your medical history and health status. Conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or sexually transmitted infections can affect pregnancy. A comprehensive checkup (blood tests, hormone profile, and imaging studies) will help you start off on the right foot. Nutrition and supplements A balanced diet and the right supplements are key: Folic acid: at least 400 µg daily, starting 3 months before conception. Iron: 18 mg per day. Calcium: 1,000 mg per day. Vitamin D: 600 IU per day. Choose whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Avoid extreme diets. How to monitor fertility and ovulation Track your menstrual cycle by recording daily basal body temperature and changes in cervical mucus. Use a fertility app or calendar and consider ovulation kits (LH tests) to pinpoint your fertile window more accurately. Lifestyle and fertility Quit smoking and limit alcohol. Maintain a BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 kg/m². Do moderate exercise: 150 minutes of aerobic activity per week. Manage stress with yoga, meditation, or therapy. Review medications and medical conditions Some drugs—antidepressants, antihypertensives, anticonvulsants—can affect fertility or fetal development. Do not stop or change doses without consulting a specialist in Assisted Reproduction. Advanced reproductive options If after 6–12 months of trying (depending on age) you haven’t conceived, consider assisted reproduction. At Ingenes we offer everything from ovulation induction and IUI to IVF: A Complete Guide, always tailored to your needs. We assess sperm quality, ovarian reserve, and uterine health to recommend the best path. For more information, see our Comprehensive Guide to Reproductive Medicine. Emotional well-being with Ingenes We know trying to conceive can be an emotional roller coaster. That’s why we offer counseling, support groups, and stress-management workshops so you and your partner feel supported, informed, and empowered. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) How long should I take folic acid? Start at least 3 months before conception with 400 µg daily. Consult your specialist if you need higher doses (up to 4 mg/day) based on your history. Does stress affect fertility? Yes. Chronic stress alters hormones like cortisol and prolactin and can impair ovulation and sperm production. Relaxation techniques and emotional support improve your chances. When should I see a fertility specialist? Under 35: after 12 months of trying without protection. Over 35: after 6 months. If you have conditions like PCOS or endometriosis, seek help sooner. Do men get tested too? Male fertility accounts for 40–50% of cases. A semen analysis evaluates count, motility, and morphology. Depending on results, hormonal or genetic tests may be required. Sources American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2021). Practice Bulletin No. 200: Early Pregnancy Loss. Obstetrics & Gynecology, 136(4), e139–e153. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000004554 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Preconception Health and Healthcare. https://www.cdc.gov/preconception/index.html MedlinePlus. (2023). Folic Acid. https://medlineplus.gov/folicacid.html Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. (2020). Diagnostic evaluation of the infertile female. Fertility and Sterility, 113(3), 545–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2019.11.014 We’re with you every step of the way. If you have questions or want a personalized plan, consult an assisted reproduction specialist for the best care.

Rebeca pasó por un diagnóstico de ovario poliquístico, endometriosis y una cirugía innecesaria, antes de lograr a sus bebés in vitro. Conoce su historia aquí.

Aneuploidía es una alteración genética que puede presentarse en el embrión y comprometer su desarrollo. Te decimos cuáles son sus principales causas y cómo prevenirla.
dación In Vitro o Fertilización In Vitro (FIV) es, actualmente, el método más eficaz de reproducción asistida. Aquí, te brindamos una guía con todo lo que necesitas saber sobre la FIV.

In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a commonly used assisted reproductive technology that has brought joy to many families worldwide. If you’re considering IVF, it’s crucial to understand its significant steps, one of the most important being embryo transfer. Let’s delve deeper into this exciting and crucial stage. What is Embryo Transfer? Embryo transfer in IVF is the process where a fertilized egg (now called an embryo) is placed into a woman’s uterus with the hope of achieving pregnancy. It is performed by a specialist using a soft and thin catheter under ultrasound guidance. This process is typically painless and requires no anesthesia. The Journey to the Embryo Transfer Before embryo transfer, the steps taken are essential in creating a healthy embryo. It starts with ovarian stimulation, where you will take medications to stimulate the growth of multiple eggs. These eggs are then retrieved in a minor procedure. After the egg retrieval, the eggs are fertilized with sperm in a lab to create embryos. These embryos are cultured for a few days while their quality and development are closely monitored. The Big Day: The Embryo Transfer Embryo transfer is a significant step in the IVF process. It’s crucial to ensure that the conditions are optimal for the embryo to implant successfully in the uterus. During the procedure, the selected high-quality embryo is gently transferred through the cervix and into the uterus. This procedure is usually quick and painless. After the transfer, you’ll rest for a short while before you can go home. You should take it easy for the next few days, but you can return to most of your normal activities. The Two-Week Wait The period after the embryo transfer and before you can take a pregnancy test is often called the “two-week wait.” It can be a period of anxiety and anticipation. Remember to take care of yourself during this time, both physically and emotionally. Understanding the Journey Each IVF journey is unique, and not every cycle results in a pregnancy. If the first attempt is unsuccessful, don’t lose heart. Our team of fertility experts is committed to supporting you every step of the way and discussing the next steps if needed. Embryo transfer is a significant step in your IVF journey. Understanding what it involves can help you feel more prepared and less anxious. We’re here to guide you through every step of your journey towards parenthood. Remember, patience and perseverance are key in this process. Believe in yourself, and never lose hope.

El síndrome de ovario poliquístico es un desajuste hormonal, conoce sus síntomas, cómo afecta tu fertilidad y las opciones para tener un bebé.

Después de los 35 años, Cisne tuvo un embarazo con FIV y logró a sus 2 bebés, aún viviendo con ovario poliquístico. Ella te cuenta su historia.

Ingenes Morelia nació para ayudar a que más personas en el occidente de México logren un bebé, con apoyo de la Reproducción Asistida.

El esperma para la inseminación artificial debe ser de un donante o pareja, nunca del especialista. Descubre por qué en Ingenes no sucedería esto.

Baja reserva ovárica y FIV positiva en su tercer intento, conoce a Claudia, quien se convirtió en mamá después de varios tratamientos fallidos.